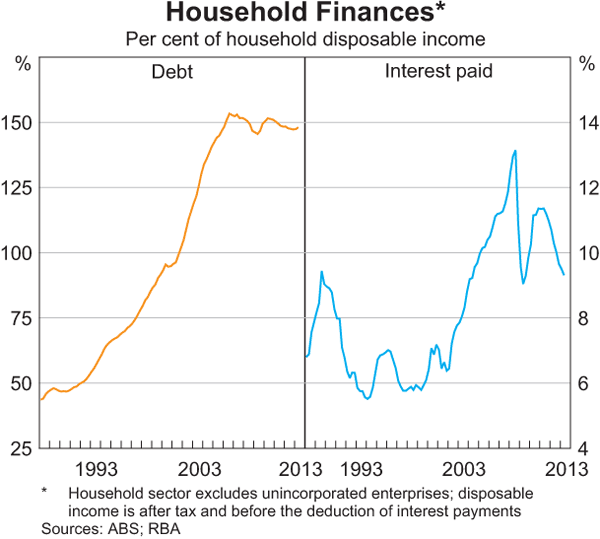
Yield Curve
The yield curve is one of the best predictors of US economic recessions. Every time the yield curve has turned negative in the last fifty years, a recession has followed.
First of all, what is a yield curve? It is the plot of yields on bonds, normally Treasuries, against their maturities. Long maturity bonds are expected to have higher yields than short-term bills, to compensate for the increased risk (primarily of interest rate changes). If you tie your money up for longer, you would expect a higher return. Hence a rising yield curve.
A rising yield curve is a major source of profit to the banks as their funding is mostly short-term while they charge long-term rates to borrowers, pocketing a healthy interest margin.
When the Fed steps into the market, however, restricting the flow of money into the economy, then short-term rates rise faster than long-term rates and the yield curve can invert (referred to as a negative yield curve).
Bank interest margins are squeezed — it is no longer profitable to borrow short and lend long — and they restrict the flow of new credit.
Credit is the lifeblood of the economy and activity slows.
The chart below compares US recessions to the yield differential: the difference between 10-year Treasury yields and the yield on 3-month T-bills. The yield differential falls below zero when 3-month T-bills yield more than 10-year T-notes.

You can see that every time the yield differential dips below zero it is followed by a gray bar indicating a recession. There is one exception: the phantom recession of 1966 when the S&P 500 fell 22%. This was originally certified as a recession by the NBER but they later changed their mind and airbrushed it out of history.
You can also see that the yield differential is declining at present but, at 2.0%, it is a long way from a flat or negative yield curve. This supports my argument last week that current Fed rate hikes are more about normalizing interest rates than about monetary tightening.
That could change in the future but at present the bull market still appears to have plenty in the tank.
Corporate Bond Spreads
Corporate bond spreads — the yield difference between high-grade corporate bonds and the risk-free Treasury rate — are another useful indicator of the state of the economy.
Wide bond spreads indicate increased risk of corporate default. Investors are concerned about the state of the economy and demand a higher premium for taking credit risk.
Narrow spreads suggest that credit premiums are low and confidence in the economy is good.
If we examine the chart below, bond spreads are declining, indicating confidence in the US economy, with even the lowest investment grade BBB dipping below 150 basis points (or 1.50%). This is synonymous with a bull market.

Australian corporate bond spreads are higher than the US, with BBB still at 200 bps. They have also declined over the last year but seem to be trending upward from their 2013 low. This is not conclusive as the current trough is not yet complete, but a higher low would warn that credit risk is rising.

Only when the tide goes out do you discover who’s been swimming naked.
~ Warren Buffett