From the Trading Diary:
I received a message from a US reader suggesting I should “stay out of politics”.
I would love to stay out of politics. Frankly, I find it tiresome. Unfortunately, politics and the economy are so intertwined as to make the study of one meaningless without consideration of the other. I say “unfortunately” because a lot of the damage done to the economy is caused by the political system.
As for Donald Trump, I am a conservative but do not support him. He is not another Reagan who can lead from the center and inspire his country. If anything he is a polarizing force, more ego-driven than Nixon and just as unpredictable.
I hope I am wrong. Trump has many sound policies and has made some solid appointments to his team. Don’t believe everything you read from a hostile media. They could do a lot of good. Provided they are able to manage the elephant in the lifeboat — the destabilizing side of Trump’s nature.
Now that I have offended at least half of all US readers — slightly less than half if you listen to bleating about the majority vote — let me explain why politics and economics are so intertwined.
Apart from trade wars, which I will discuss at a later date, I see the main threat to the US economy as inflation.
Before I start, let me say that these dangers are not immediate and the present boom is likely to continue for the next 12 to 18 months. But they could quickly materialize, bringing the boom to a premature end, so it is best to keep a weather eye on them.
Inflation
Earlier this week I discussed why the inflation outlook is so important to stock market performance:
From Tim Wallace at The Sydney Morning Herald:
Nine years on from the start of the financial crisis, the US recovery may be overheating, Legal & General Investment Management economist James Carrick has warned.
He has predicted a series of interest rate hikes will tip the US into a 2018 recession.”Every recession in the US has been caused by a tightening of credit conditions,” he said, noting inflation is on the rise and the US Federal Reserve is discussing plans for higher interest rates.
Officials at the Fed have only raised interest rates cautiously, because inflation has not taken off, so they do not believe the Fed needs to take the heat out of the economy.
But economists fear the strong dollar and low global commodity prices have restricted inflation and disguised domestic price rises. Underneath this, they fear the economy is already overheating.
As a result, they expect inflation to pick up sharply this year, forcing more rapid interest rate hikes.
That could cause a recession next year, they say. In their models, the signals are that this could take place in mid-2018.
Harvard scholar Paul Schmelzing points out that inflation is starting to rear its head in both China and Germany, with producer prices rising. This may in part be a result of the falling value of the Yuan and Euro against the Dollar, resulting in higher domestic commodity prices.
The opposite, however, is true for the US, with a rising Dollar lowering import prices and acting as a headwind against inflation.
The consumer price index (CPI) is rising because of higher crude oil prices but core CPI (excluding food & energy) has remained fairly constant, around the 2.0 percent target, over the last five years.

So why the concern?
Well the Fed is more concerned about underlying inflation, best reflected by hourly wage rates, than the headline CPI figure.
A sharp rise in hourly earnings rates would force the Fed to respond with tighter monetary policy to take the heat out of the economy.
The chart below shows how the Fed slams on the brakes whenever average hourly earning rates grow above 3.0 percent. Each surge in hourly earnings is matched by a dip in the currency growth rate as the Fed tightens the supply of money to slow the economy and reduce inflationary pressure. And tighter monetary normally leads to recession.
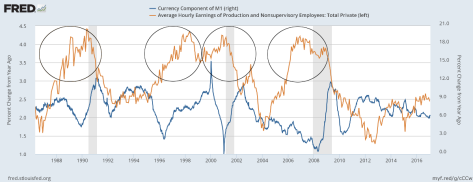
Two anomalies on the above chart warrant explanation. First, is the sharp upward spike in currency growth in 1999/2000 when the Fed reacted to the LTCM crisis with monetary stimulus despite high inflationary pressures. Second, is the sharp dip in 2010 when the Fed took its foot off the gas pedal too soon after the financial crisis of 2008/2009, mistaking it for a regular recession.
Hourly earnings growth is currently at 2.5 percent, so the Fed has some wiggle room and is only likely to react with tighter monetary policy when the figure reaches 3.0 percent.
Recent rate rises are more about normalizing interest rates — not taming inflation — and are not cause for alarm.
But Paul Schmelzing warns that the combination of a tight labor market and fiscal stimulus could fuel inflation and lead to a bear market in bonds similar to the 1960s.
That is exactly where Donald Trump is headed with a major infrastructure program likely to hit the ground next year. In a tightening labor market, the Fed would be forced to tighten monetary policy, slowing the economy and leading to another bear market in stocks as well as bonds.
Politics is tricky; it cuts both ways. Every time you make a choice, it has unintended consequences.
~ Stone Gossard



